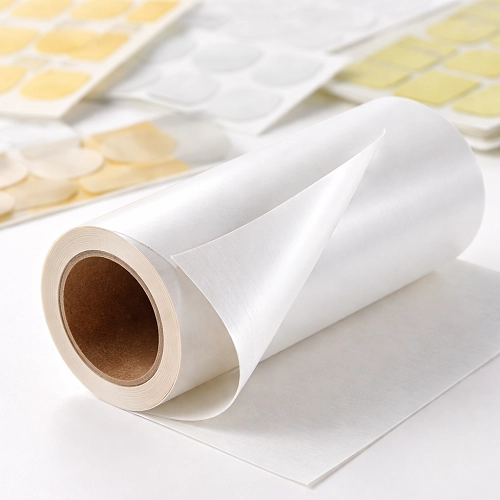
Engineering Release Liner Paper for Adhesive and Label Applications
Release liner paper is a ubiquitous but often overlooked material that plays a crucial role in numerous industries—from adhesives and packaging to medical products and electronics. At its core, release liner paper serves as a temporary carrier for materials that have tacky, adhesive, or sensitive surfaces.
What Is Release Liner Paper?
Release liner paper is a specialized paper or film substrate coated with a release agent on one or both sides to enable clean and easy separation of an adhesive layer or other tacky material. Once the adhesive-backed product (such as tape, label, or sticker) is ready for application, the release liner is peeled away, exposing the functional surface without damage or contamination.
Composition and Structure
Release liner paper is a multi-layer engineered product.
Its performance derives from the interaction between:
1. Base Material (Substrate)
The foundation of release liner paper is the base substrate, typically made from:
- Kraft paper – strong and flexible, widely used
- Glassine paper – smooth and dense, excellent for high-quality graphics
- Bleached paper – clean appearance and good dimensional stability
- Synthetic films (e.g., PET, PP) – for high-temperature or precision applications
Each substrate has trade-offs in terms of strength, surface smoothness, moisture resistance, and cost.
2. Release Coating
The release coating is the heart of release liner performance. It reduces the adhesion between the liner and the adhesive layer.
Common release systems include:
- Silicone coatings (predominantly) – provide low, controlled release forces
- Fluorochemicals – for specialized ultra-low adhesion needs
- Organic release agents – used in biodegradable or specialty applications
Release coatings can be applied on one side (single-side) or both sides (double-side) of the substrate, depending on the product design.
3. Surface Treatments
To ensure proper adhesion of the release coating and product consistency, substrates often undergo pre-treatments such as:
- Corona discharge
- Flame treatment
- Chemical priming
These processes modify the surface energy of the paper for better coating uniformity.
Functional Mechanisms
The purpose of release liner paper is to control:
Release Force
This is the force required to peel the liner away from the adhesive.
It must be:
- High enough to keep the adhesive protected and intact during storage and handling
- Low enough to allow easy removal without damaging the product or leaving residue
Release force is influenced by factors such as coating chemistry, application technique, ambient conditions, and dwell time (how long the adhesive and liner remain in contact).
Slip and Anti-Static Properties
Many liners incorporate additional features:
- Slip additives – to facilitate smooth unwinding and processing
- Anti-static agents – to reduce static cling, especially in high-speed converting operations
Manufacturing Processes
The production of release liner paper involves several key steps:
Paper Production
Depending on the desired liner properties, base paper is produced with specific fiber blends, calendering (for smoothness), and thickness (usually measured in microns or pounds per ream).
Surface Treatment
Before coating, surface treatments (e.g., corona) increase surface energy to promote uniform coating adhesion.
Coating Application
Release coatings are applied via:
- Roller coating
- Slot die coating
- Curtain coating
- Spray coating
Precise control over coat weight and uniformity is critical to consistent liner performance.
Drying and Curing
Coatings are dried or cured to achieve the desired release characteristics. Temperature, dwell time, and line speed are controlled for quality.
Slitting & Rewinding
After coating and curing, the wide liner rolls are slit to specific widths and rewound into rolls for shipment to converters and end users.
Key Performance Metrics
To evaluate release liner paper, several technical metrics are used:
| Metric | Description |
| Release force | Force needed to peel liner from adhesive |
| Coefficient of friction (COF) | Affects unwind and processing behavior |
| Tensile strength | Measures liner robustness |
| Moisture content / Dimensional stability | Important for consistent performance |
| Surface smoothness / Roughness | Affects coating quality and release behaviour |
Types of Release Liners
Release liners can be classified by:
By Substrate
- Kraft paper liners
- Glassine paper liners
- Polyester (PET) liners
- Polypropylene (PP) liners
By Coating Configuration
- Single-side release
- Double-side release
- Gradient release (different release levels on each side)
By End-Use Specialty
- Medical grade liners (biocompatible and low particulate)
- High-temperature liners (for industrial tapes)
- Printed liners (with branding and product info)
End-Use Applications
Release liner paper is integral to many segments:
Pressure-Sensitive Labels
Liners protect adhesives on labels and are critical for dispensing performance in printers and applicators.
Adhesive Tapes
From packaging tape to specialty industrial tapes, liners provide a barrier until use.
Graphics and Protective Films
Liners enable precise application of decals, window films, and surface protection materials.
Medical Products
Used in wound dressings, transdermal patches, and surgical adhesives where hygiene and controlled release are paramount.
Electronics and Industrial Converters
Liners support flexible circuits, thermal interface materials, and other precision components during handling.
Challenges and Innovations
Sustainability
Traditional release liners contribute to waste, especially in single-use applications.
Industry trends focus on:
- Recyclable liner systems
- Compostable coatings
- Linerless technologies (reducing waste by eliminating release liners entirely)
Performance Enhancements
Research continues into advanced coatings that deliver:
- Tunable release profiles
- Improved thermal stability
- Reduced dependency on silicone in certain niches
Release liner paper is an engineered material that quietly enables many products and processes we take for granted. From its substrate and surface chemistry to its precision manufacturing and performance metrics, release liners are a blend of materials science and practical design. As sustainability and performance demands grow, so too will innovation in this foundational material.